Sustainability
SUPPORT THE UNITED NATIONS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
We have incorporated the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into our business development strategy and are committed to aligning the responses of our stakeholders with the relevant sustainable development goals (SDGs) to actively promote the integration of operational development and sustainable development value.
HIERARCHICAL GOVERNANCE STRUCTURE FOR ESG INITIATIVES
STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT
Long-term and effective communication with stakeholders is the top priority for improving sustainable development. During the Reporting Period, the Group evaluated material topics to important stakeholders including employees, investors, customers, suppliers and contractors through online questionnaires. By analyzing the survey results of the Group’s management and other stakeholders, the topics identified by the Group’s management and other stakeholders as having a significant impact on the Group’s economy, society and environment are summarised. The Group fully understands their demands and expectations and incorporates them into the Group’s sustainable development management policy.
| Stakeholder Groups | Communication Channels | Issues of Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Management |
|
|
| Employees |
|
|
| Customers |
|
|
| Shareholders/investors |
|
|
| Suppliers/contractors |
|
|
| Community |
|
|
TACKLING CLIMATE CHANGE
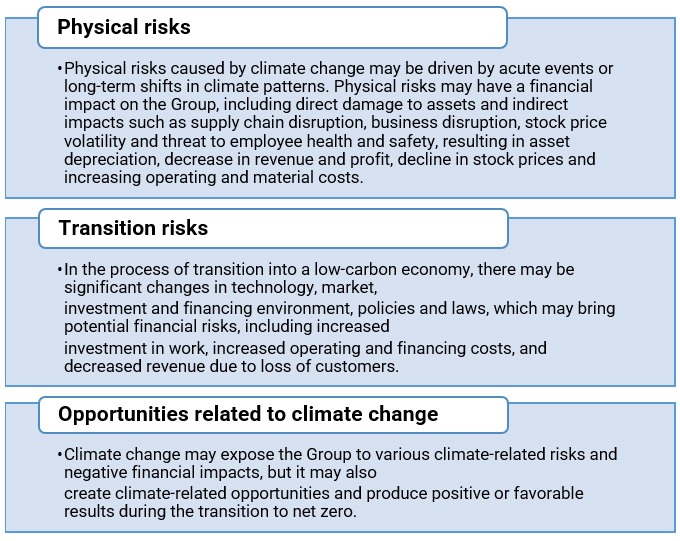
The Group is well aware of the significant impact of climate change on the global and the Group’s business operations. In the face of the increasingly severe climate change threats, the Group has carried out climate-related risks and opportunities assessment in accordance with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) since 2020. In 2022, the Group launched a new round of climate change questionnaire assessment added a matrix analysis based on the assessment result to further improve the integrity and transparency of climate-related information disclosure, and more intuitively demonstrate the short, medium and long-term climate-related risks and opportunities identified.
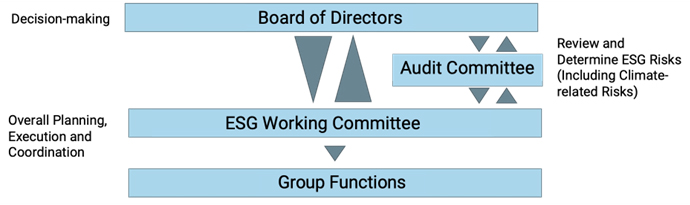
Governance
The Board of Directors of the Group is fully responsible for the work related to climate change. The ESG Working Committee ensures that the relevant requirements are met and makes recommendations, and reports to the Board at least once a year. The Board reviews and determines the risk management matters related to climate change through the Audit Committee.
| Responsibilities of the Board and the ESG Committee | |
|---|---|
| Duties of the Board: | Supervise and make final decisions on climate change-related matters, including annual review of climate change management, identify climate change risks and opportunities, countermeausres, and relevant disclosures and announcements. |
| Duties of the ESG Working Committee: | Regular meetings are held to identify risks and opportunities of climate change; formulate climate change management strategies, policies and systems, measures and goals for the Board to make decisions; ensure distribution and completion of specific items of work, and supervise performance of subsidiaries and affiliates in implementation of relevant measures. |
Strategies
The Group agreed that scenario analysis can help to explore and understand the impact of various climate-related risks, including transition and physical risks, on business, strategy and financial performance with the lapse of time. Following TCFD’s recommendations, the Group selected RCP 8.5 – the baseline scenario of the highest greenhouse gas emissions as a conservative forecast for the physical risk assessment, and assessed the transition risks related to climate with IEA 2DS – the International Energy Agency Sustainable Development Scenario.
RCP 8.5 scenario: Under this scenario, there is no new climate change policy in the world to predict and limit emissions. It is estimated that by 2050, the global average temperature will increase by 2.3 degrees Celsius compared to the early stage of industrialization, and by 2100, the sea level will increase by approximately 0.43 meters.
IEA 2DS scenario: The scenario assumes a high level of global sustainable development by 2050. Through various new policy requirements and measures, the global warming is controlled within 2.0 degrees Celsius and the climate change and air pollution issues are effectively addressed.
For a detailed description of the risks and opportunities, please refer to the “Climate-related Risks and Opportunities Management” section.
Climate-related Risks and Opportunities Management
The Group actively responded to global climate change and continued to pay attention to climate-related risks and opportunities. Based on the results of the 2022 questionnaire assessment, the identified risks and opportunities were ranked in accordance with the two dimensions of “potential risks (degree of impact)” and “impact time period”, and the following matrix was determined.
Key performance
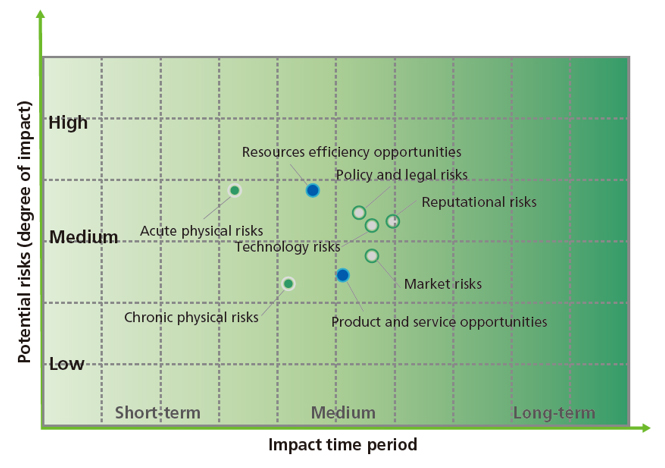
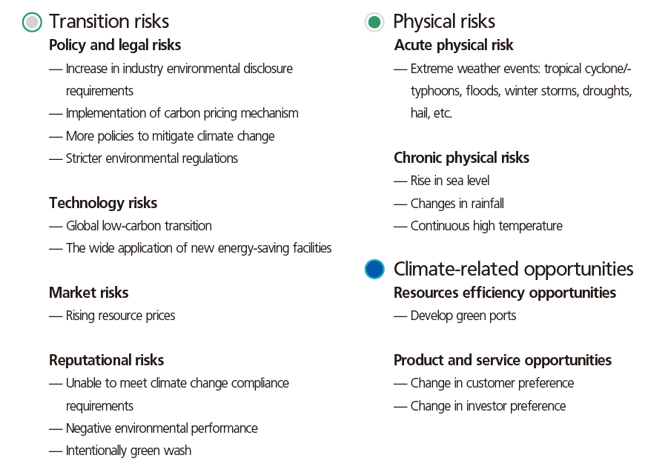
Impact analysis
| Risk description | Potential financial impact | Impact boundary | Actions undertaken |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical risks | |||
| Acute physical risks | |||
| Risks driven by extreme weather events, such as typhoons, hurricanes or floods, flooding the port or swamping the port, making the port not able to operate normally, damage to terminals, operating facilities, equipment, storage areas and cargoes, lead to siltation of port waterways. |
|
Short-medium term |
|
| Chronic physical risks | |||
| The long-term change in climate patterns and the incremental changes in climate (rising in sea level, changing in rainfall and continuous high temperatures) have led to more frequent and severe extreme events, leading to more frequent transportation delays and affecting the reliability of marine transportation. |
|
Medium |
|
| Transition risks | |||
| Policy and legal risks | |||
| Directly or indirectly affected by policies and laws designed to limit the impact of climate change and/or enhance the adaptability to climate change, including the implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms, increase in environmental disclosure requirements and stricter environmental and climate policies, and increased corporate compliance |
|
Medium |
|
| Technology risks | |||
| Directly or indirectly affected by technological changes, including the industry’s support for global low-carbon transformation to increase research and development and investment in renewable energy technologies, the wide application of new energy-saving facilities to procure new facilities and replace old equipment (Increased investment in the development of smart green ports in the industry) |
|
Medium |
|
| Reputational risks | |||
| Stricter environmental regulations may expose enterprises to higher risks of claims and litigation |
|
Medium-long term |
|
| Market risks | |||
| Climate change affects the supply and demand of certain goods, products and services in the market, including the increase in resource prices (such as energy, sales of fuel,etc.) |
|
Medium |
|
| Opportunities description | Potential financial impact | Impact boundary | Actions undertaken |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resources efficiency opportunities | |||
| In the medium-long term, improving energy efficiency can directly save operating costs and contribute to limiting global carbon emissions, including the development of green ports, the use of clean energy and the promotion of shore-based power use. |
|
Medium |
|
| Product and service opportunities | |||
| The innovation and development of low-carbon emission products and services can enhance the market competitiveness, such as customers’ preference for more environmentally friendly service providers or products (such as low-carbon marine fuel), and investors’ preference towards focusing on investing in green port operators. |
|
Medium |
|
Metrics and Targets
The Group measures and discloses indicators related to greenhouse gases and energy to monitor climate change management performance, including gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2), greenhouse gas emission intensity (in terms of turnover), energy consumption (electricity, diesel, LNG, natural gas and heat), energy consumption intensity (in terms of turnover).
LABOR MANAGEMENT POLICIES ON EMPLOYEE DIVERSITY AND INCLUSION, WOMEN’S PROTECTION
The Group considers talent management as the cornerstone of corporate development and sustainable management, and is committed to creating an equal and healthy workplace environment. We are determined to eliminate any form of discrimination on gender, race, religion, age and physical condition. The Group supports the employment of disabled persons and protects the rights and interests of female employees in accordance with relevant and regulations such as the Measures for the Administration of Employment Security Fund for the Disabled in Tianjin and the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Women’s Rights and Interests.
TALENT TEAM BUILDING


